Over 50 years ago, we were introduced to the concept of box wine – a wine that came in a box with a collapsible bag inside. The invention gained popularity because it was cheaper than other wines and spirits. Adding the integral tap in the bag made it easier to pour a glass of wine and store it. From an environmental standpoint, boxed wine is recyclable and easier to transport. Although glass is recyclable, it requires a lot of energy to produce and transport.
Switching to cardboard is less energy-intensive to produce and is a lot lighter in comparison to transport. Although boxed wine has been associated with being a cheaper quality wine, the quality has improved significantly over the years, with many winemakers packaging their products in boxes.
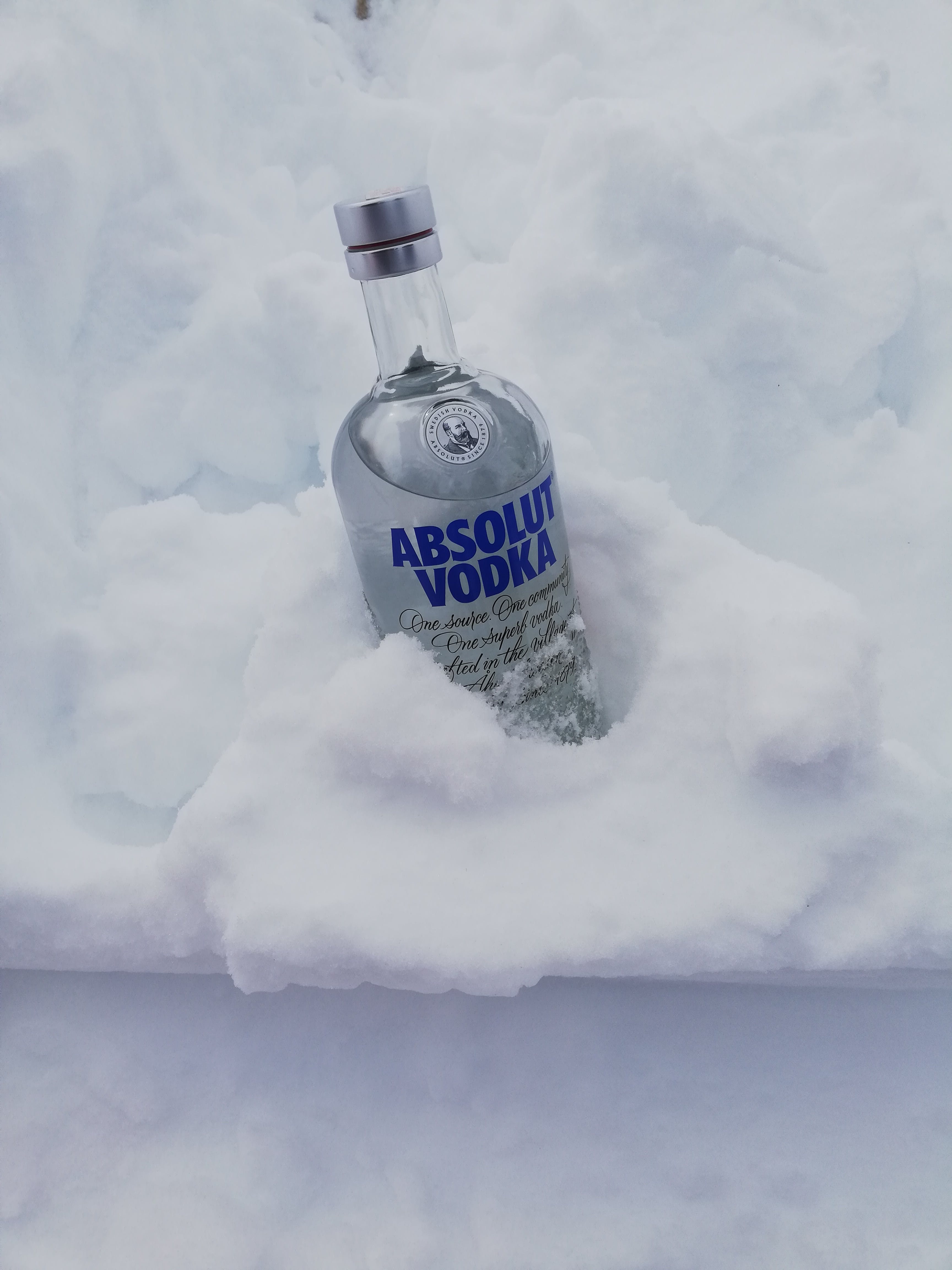
If wine can be packaged more sustainably, what about other types of alcohol? Swedish company Absolut Vodka wants to switch from glass bottles to paper bottles. As part of a pilot project, Absolut has made bottles out of 57% wood fibres certified by the Forest Stewardship Council. To prevent the liquid from leaking through, the bottles contain an integrated moisture barrier made from recycled plastic.
This pilot project is part of a collaboration with Paboco and the Pioneer Community. Paboco is a paper bottle company working towards creating the world’s first 100% bio-based and recyclable paper bottle. The paper bottle is recyclable as paper packaging and can be designed to hold many different products, from soda to sun location. The company has partnered with L’Oreal, the Coca-Cola Company, Procter & Gamble and many others to help introduce smarter and more sustainable packaging solutions into more significant markets.
Paboco is no stranger to packaging alcohol in paper bottles. They have been successful with beer company Carlsberg with their Fibre Bottle, made out of plant-based PEF polymer lining. The material is compatible with plastic recycling systems and can degrade in nature. The PEF, which is made out of natural raw materials, protects the taste and fizziness of the beer, and the outer shell helps to keep the beer colder for longer compared to cans or glass bottles.
Absolut Vodka has been testing these paper bottles for over a decade, and they are finally launching 500-millilitre paper bottles in select Tesco stores in Manchester, in the UK. The city of Manchester was chosen as a testing site because it had the recycling infrastructure to handle the bottles. Absolut also found that Manchester had higher household recycling rates than any other region in the UK.
Much like how wine boxes are lighter and less energy-intensive to transport, Absolut will calculate the carbon footprint of the paper bottles, which will be significantly lighter than their traditional glass bottles. The company is also collecting feedback from consumers, retailers and distributors and will use their findings to make necessary adjustments. They will also be working on developing ways to make the bottles from more than 57% paper and achieve a 100% paper bottle target.
While glass is a better option and can be used infinitely, compared to plastic bottles, it is pretty costly to recycle. Glass can only be recycled in furnaces that use high energy to reach high heat, increasing pollution. The switch to paper bottles could have a significant impact on the emission that comes from the food and drink industry. While Absolut Vodka is only one of many alcohol companies, it could be the inspiration needed to make the switch. We might see our liquor stores go from clanky, heavy glass bottles to lightweight paper ones in the near future.
Source Happy Eco News