In a small room near the Alps in northern Italy, containers filled with millions of crickets are stacked on top of each other.
Jumping and chirping loudly – these crickets are about to become food.
The process is simple: they are frozen, boiled, dried, and then pulverised.
Here at the Italian Cricket Farm, the biggest insect farm in the country, about one million crickets are turned into food ingredients every day.
Ivan Albano, who runs the farm, opens a container to reveal a light brown flour that can be used in the production of pasta, bread, pancakes, energy bars – and even sports drinks.
Eating crickets, ants and worms has been common in parts of the world like Asia for thousands of years.
Now, after the EU approved the sale of insects for human consumption earlier this year, will there be a shift in attitudes across Europe?
“We will oppose, by any means and in any place, this madness that would impoverish our agriculture and our culture,” Deputy Prime Minister Matteo Salvini wrote on Facebook.
But is that all about to change? Several Italian producers have been perfecting cricket pasta, pizza and snacks.
“What we do here is very sustainable,” says Ivan. “To produce one kilo of cricket powder, we only use about 12 litres of water,” he adds, pointing out that producing the same quantity of protein from cows requires thousands of litres of water.
Farming insects also requires just a fraction of the land used to produce meat. Given the pollution caused by the meat and dairy industry, more and more scientists believe insects could be key to tackling climate change.
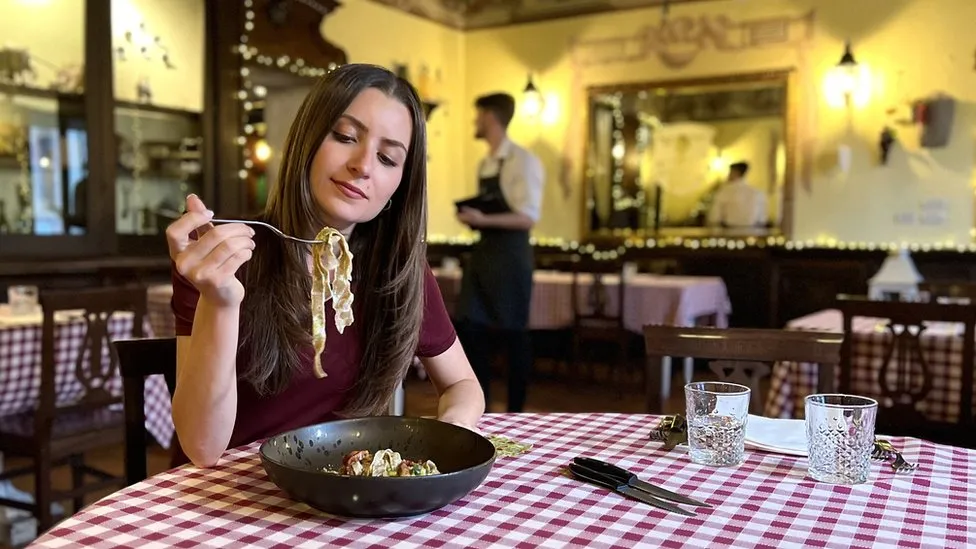
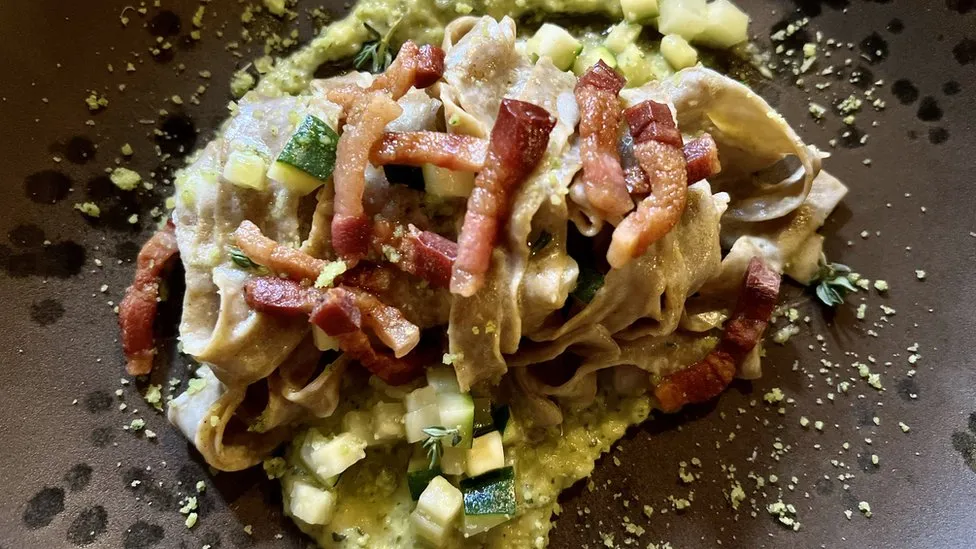
At a restaurant near Turin, chef Simone Loddo has adapted his fresh pasta recipe, which dates back nearly 1,000 years – the dough is now 15% cricket powder.
It emanates a strong, nutty smell.
Some of the diners refuse to try the cricket tagliatelle, but those who do – including me – are surprised at how good it tastes.
Aside from the taste, cricket powder is a superfood packed with vitamins, fibre, minerals and amino acids. One plate contains higher sources of iron and magnesium, for example, than a regular sirloin steak.
But is this a realistic option for those who want to eat less meat? The main issue is the price.
“If you want to buy cricket-based food, it’s going to cost you,” says Ivan. “Cricket flour is a luxury product. It costs about €60 (£52) per kilogram. If you take cricket pasta for example, one pack can cost up to €8.”
That’s up to eight times more than regular pasta at the supermarket.
For now, insect food remains a niche option in Western societies, as farmers can sell poultry and beef at lower prices.
“The meat I produce is much cheaper than cricket flour, and it’s very good quality,” says Claudio Lauteri, who owns a farm near Rome that’s been in his family for four generations.

But it’s not just about price. It’s about social acceptance.
Across Italy, the number of people living to the age of 100 and beyond is rising fast. Many point to the Mediterranean diet as the Holy Grail for a healthy lifestyle.
“Italians have been eating meat for centuries. With moderation, it’s definitely healthy,” says Claudio.
He believes that insect food could be a threat to Italian culinary tradition – which is something universally sacred in this country.
“These products are garbage,” he says. “We are not used to them, they are not part of the Mediterranean diet. And they could be a threat for people: we don’t know what eating insects can do to our bodies.
“I’m absolutely against these new food products. I refuse to eat them.”
While insect farming is increasing in Europe, so too is hostility towards the idea.
The EU decision to approve insects for human consumption was described by a member of Italy’s ruling far-right Brothers of Italy party as “bordering on madness”.
Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni, who has referred to Italy as a “food superpower”, created a Made in Italy ministry when she was elected, with the aim of safeguarding tradition.
“Insect products are arriving on supermarket shelves! Flour, larvae – good, delicious,” she said in a tone of disgust in a video.
Amid concerns that insects might be associated with Italian cuisine, three government ministers announced four decrees aimed at a crackdown. “It’s fundamental that these flours are not confused with food made in Italy,” Francesco Lollobrigida, the agriculture minister, said.

Insect food is not just dividing opinions in Italy.
In Poland, it has become a hot topic ahead of an election this year. In March, politicians from the two main parties accused each other of introducing policies that would force citizens to eat insects – the leader of the main opposition party, Donald Tusk, labelled the government a “promoter of worm soup”.
Meanwhile, Austria, Belgium and the Netherlands are more receptive to eating insects. In Austria, they eat dried insects for aperitivo, and Belgians are open to eating mealworms in energy shakes and bars, burgers and soups.
“Unfortunately there’s still a lot of misinformation about eating insects,” says Daniel Scognamiglio, who runs the restaurant that serves the cricket tagliatelle.
“I have received hate, I have been criticised. Food tradition is sacred for many people. They don’t want to change their eating habits.”
But he has identified a shift, and says more people – often out of curiosity – are ordering cricket-based products from his menu.
With the global population now exceeding eight billion, there are fears that the planet’s resources could struggle to meet the food needs of so many people.
Agricultural production worldwide will have to increase by 70%, according to estimates by the UN’s Food and Agricultural Organisation.
Shifting to eco-friendly proteins – such as insects – might become a necessity.
Until now, the possibilities for producing and commercialising insect food had been limited. With the EU’s approval, the expectation is that as the sector grows, the prices will decrease significantly.
Ivan says he already has a lot of requests for his products from restaurants and supermarkets.
“The impact on the environment is almost zero. We are a piece of the puzzle that could save the planet.”
Source BBC