
Olaf Scholz will head a three-party coalition with broad plans for Germany’s transition to a green economy, under a deal to end 16 years of government led by Angela Merkel.
Almost two months after his Social Democrat party won federal elections, he will go into power with the Greens and business-friendly Free Democrats.
Climate protection forms a big part of the coalition deal.
The parties aim to phase out coal use by 2030, eight years ahead of schedule.
They will also seek to use 2% of German territory for wind power and focus on hydrogen-based energy too. By 2030, the parties want 80% of electricity to be sourced from renewable energy and 15 million electric cars to be on German roads.
There are also plans to legalise the sale of cannabis in licensed premises, with controls on the quality and distribution of the drug.
Germany is Europe’s biggest economy, so decisions taken by the new government will have a big effect on its neighbours.
In a news conference, Mr Scholz, 63, said “sovereignty of Europe is a cornerstone of our foreign policy”. He highlighted Germany’s friendship with France and partnership with the US.
He spoke of daring to make greater progress in a coalition “on equal terms”. He also pointed out that the three parties’ wider memberships still had to approve what has been labelled a “traffic-light” coalition, because of the parties’ red, yellow and green colours.

He will only take over as chancellor from Mrs Merkel after a vote in the Bundestag, expected between 6 and 9 December.
Mr Scholz will enter office during a difficult period of the Covid-19 pandemic, with Germany one of several European countries where infections have skyrocketed to record levels in recent weeks.
On Wednesday, he said the coalition would ramp up vaccinations and consider making jabs compulsory for health staff and other essential worker.
“The situation is bleak,” Mr Scholz said. “The coronavirus is still not vanquished.”
‘Biggest challenge of our time’
The Social Democrats won the 26 September vote, ahead of Mrs Merkel’s Christian Democrat alliance, which saw its worst-ever election result. The Greens achieved their best-ever result, under candidate Annalena Baerbock, who spoke of an ambitious alliance aiming to start a paradigm shift to transform the economy.
Describing the climate crisis as the biggest challenge of our time she said: “We can transform our economy so it becomes climate neutral. We have an agreement where climate neutrality is a common denominator.”
Ms Baerbock is expected to become foreign minister in the new government, while her Greens co-leader Robert Habeck gets the role of vice-chancellor as well as overseeing energy transition.
The new finance minister is set to be Christian Lindner, the Free Democrat leader whose party has a wide following of young voters. “The younger generation has given us this job to overcome the status quo of recent years,” he said.
What are their plans?
Making Germany climate neutral by 2045 is a big focus of the deal, entitled “Daring more progress”. Phasing out coal will take place “ideally” by 2030, and solar energy will become compulsory on the roofs of new commercial buildings and the general rule for new private homes. The 16 states will have to provide 2% of their area for wind power. The goal to phase out cars with internal combustion engines remains the EU’s target of 2035.
Minimum wages will rise to €12 (£10) an hour and another 400,000 new apartments will be built every year, a quarter of which will be social housing, to tackle Germany’s housing crisis.
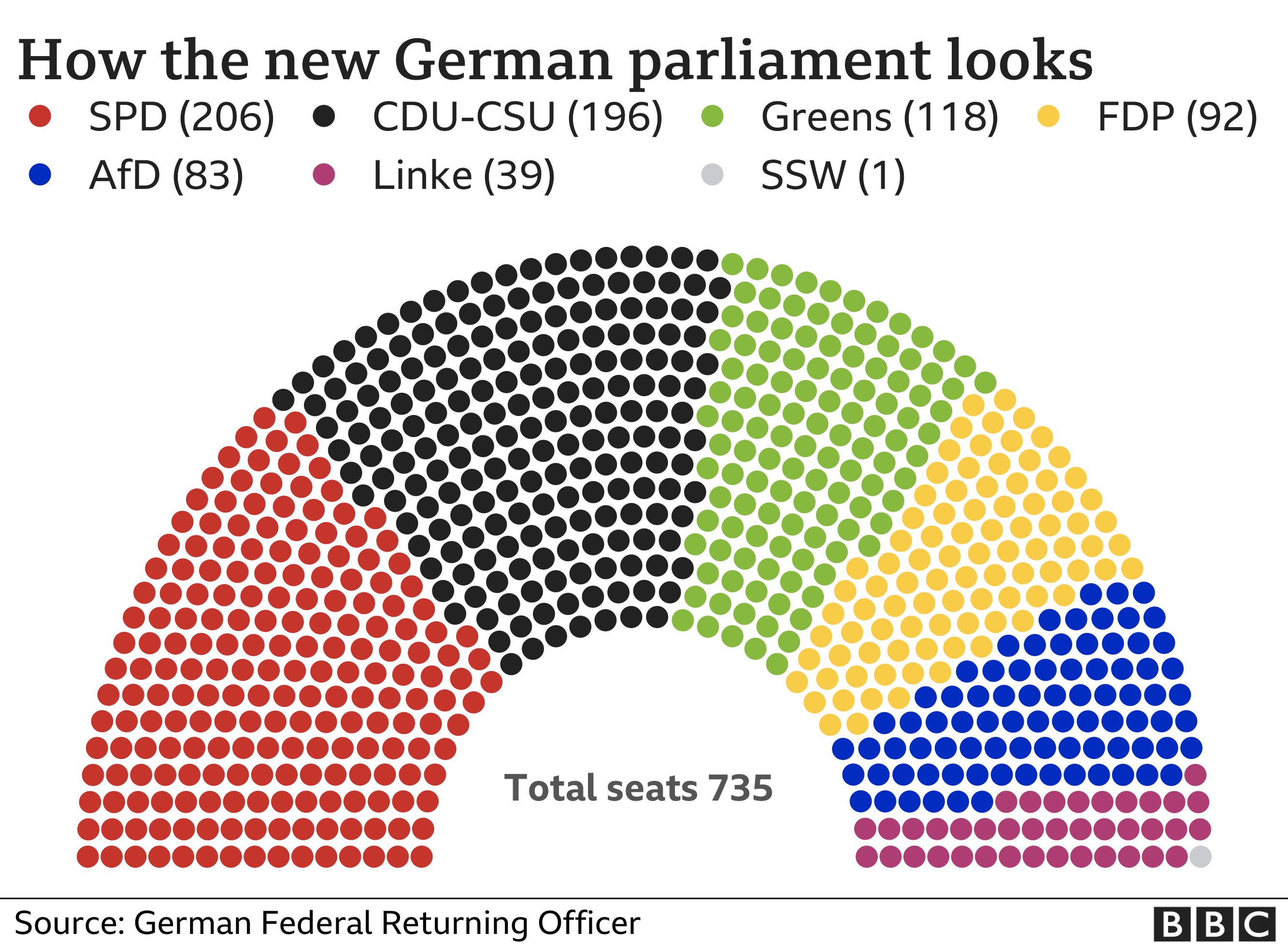
The voting age will be lowered from 18 to 16, with plans to reform electoral law to bring an end to ever-increasing numbers of MPs. The new Bundestag has 735 seats. Changing the voting age for European elections requires a simple parliamentary majority, but for federal elections it would need two-thirds support.
Immigrants will be able to apply for German citizenship after five years. They will also be allowed dual citizenship under the coalition’s plans. This would transform the lives of millions of immigrants, many of who remain foreign nationals despite having lived in Germany for decades.
A Covid crisis team will be set up at the chancellery to focus on the pandemic. Mr Scholz said vaccination was the way out of the pandemic and in some care settings involving vulnerable people it should be made compulsory. Mr Scholz said the coalition had agreed to invest €1bn in bonuses for health workers.
On foreign policy, the parties said they wanted “to raise Europe’s strategic sovereignty”, which effectively means more independence on energy, security and other international issues. However, Germany’s relationship with the US and its membership of the Nato alliance will remain central to its security.
Germany’s no-new-debt rule was lifted during the pandemic as more funds were needed to address the crisis. But by 2023, the coalition says it wants to bring back the debt brake which is enshrined in Germany’s constitution.
A ban on doctors advertising that they carry out abortions will be lifted, to enable public information to be provided about the method without fear of prosecution.
Source BBC


